Facts about Hyperopia (Farsightedness)
| Treatment Method: | Visual aids, laser correction (Femto-LASIK), or lens implantation (intraocular lenses) |
|---|---|
| Symptoms: | Blurred vision up close, clearer vision at a distance |
| Treatment Duration: | Depends on the chosen treatment method |
| Anesthesia: | Locally anesthetic eye drops |
| Clinic Stay: | Outpatient |
| Aftercare: | Depends on the chosen treatment method |
Symptoms of Hyperopia
Farsighted patients can see distant objects clearly but have difficulty seeing up close. Reading is the most commonly affected activity.
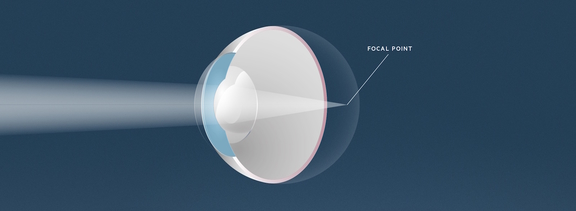
In hyperopia, the eye is usually shorter than normal. Therefore, light rays are focused (virtually) behind the retina. Optical correction is achieved by increasing the eye’s refractive power, shifting the focal point forward onto the retina.

Treatment of Hyperopia (Farsightedness)
For glasses and contact lenses, this is achieved using a convex lens, with the corrective value given in positive diopters. Hyperopia can be compensated up to a certain age by the reshaping of the eye’s lens (accommodation) when looking into the distance.
If one wishes to be independent of visual aids, patients with high hyperopia are most commonly corrected with intraocular lens implants, meaning an additional lens is implanted into the eye, allowing them to forgo glasses and contact lenses. For lower diopter values (up to +3 dpt), laser correction using Femto-LASIK is also possible.
Frequently Asked Questions About Farsightedness
How can I tell if I am farsighted?
In farsightedness, also called hyperopia, nearby objects appear blurry. Due to the eye muscles’ ability to contract, it is still possible—especially at a young age—to change the lens curvature (accommodation) to a certain extent and thereby compensate for the vision defect. For a person affected by farsightedness, much stronger accommodation is required to see clearly up close than for someone with normal vision. This often leads to symptoms such as eye or headaches, fatigue, burning sensations in the eyes, tearing, recurring conjunctivitis, or blurred vision. In children, compensating for farsightedness can cause inward turning of the eyes (esotropia or convergent strabismus). Hyperopia in childhood should always be detected early and treated if necessary, because otherwise it can lead to permanent vision impairment (so-called amblyopia).
What is farsightedness?
If there is a mismatch between the refractive power and the axial length of the eye, this is called farsightedness (hyperopia, hypermetropia). In affected individuals, a blurred image of nearby objects is formed behind the retina.
How does farsightedness develop?
Farsightedness occurs either due to insufficient refractive power of the light-bending structures (lens, cornea) with a normal axial length of the eye, or due to a too short eye axis with normal refractive power. Farsightedness can result from diseases or changes in the cornea or from inadequate axial growth. Additionally, lens displacement or absence of the lens can lead to farsightedness. Hyperopia is often hereditary.
How is farsightedness diagnosed by the eye doctor?
During an eye examination at our clinics, both the internal and external parts of the eyes are examined under magnification, allowing any diseases or disorders of specific sections of the eye to be identified as potential causes of farsightedness. Additionally, a vision test is performed to check both near and distance vision. Using lenses placed in front of the eye during a procedure called refraction assessment, the degree of deviation of the eye’s refractive media from the norm is determined. The resulting value indicates the prescription strength needed for glasses or contact lenses.
For young patients, the determination of refractive values is done with the accommodation ability switched off. This is achieved by administering special eye drops that temporarily paralyze the lens’s ability to change shape (so-called cycloplegia) for a few hours.
What is nearsightedness and farsightedness?
Patients who suffer from nearsightedness (myopia) can only see distant objects clearly — objects far away appear blurry. However, their vision up close is usually clear and unrestricted. In contrast, patients with farsightedness (hyperopia) see nearby objects as blurry or can only focus on them with increased effort.
Is farsightedness curable?
Laser therapy can change the shape, thickness, or surface of the cornea, thereby altering its refractive power. There are also lens implants that can correct farsightedness from inside the eye.
How can farsightedness be corrected?
In addition to the conservative correction of farsightedness using glasses or contact lenses, there are nowadays also options for surgical correction, which involve a permanent change to the refractive power of the cornea. During laser treatment, the superficial shape of the cornea is altered according to the vision defect. With lens implants, which can correct farsightedness inside the eye, a positive refractive artificial lens is implanted into the eye to correct the vision error.
CONTACT
Ophthalmology Clinic Linz
Weissenwolffstraße 13, 3rd Floor
4020 Linz
Office Hours
Phone Consultation Hours
MON, WED, THU 09:00 AM – 6:00 PM
TUE 09:00 AM - 4:00 PM
FRI 09:00 AM – 12:00 PM
Appointment Days
By appointment only
Ophthalmology Clinic Vienna
Habsburgergasse 10, 4th Floor
1010 Vienna






